
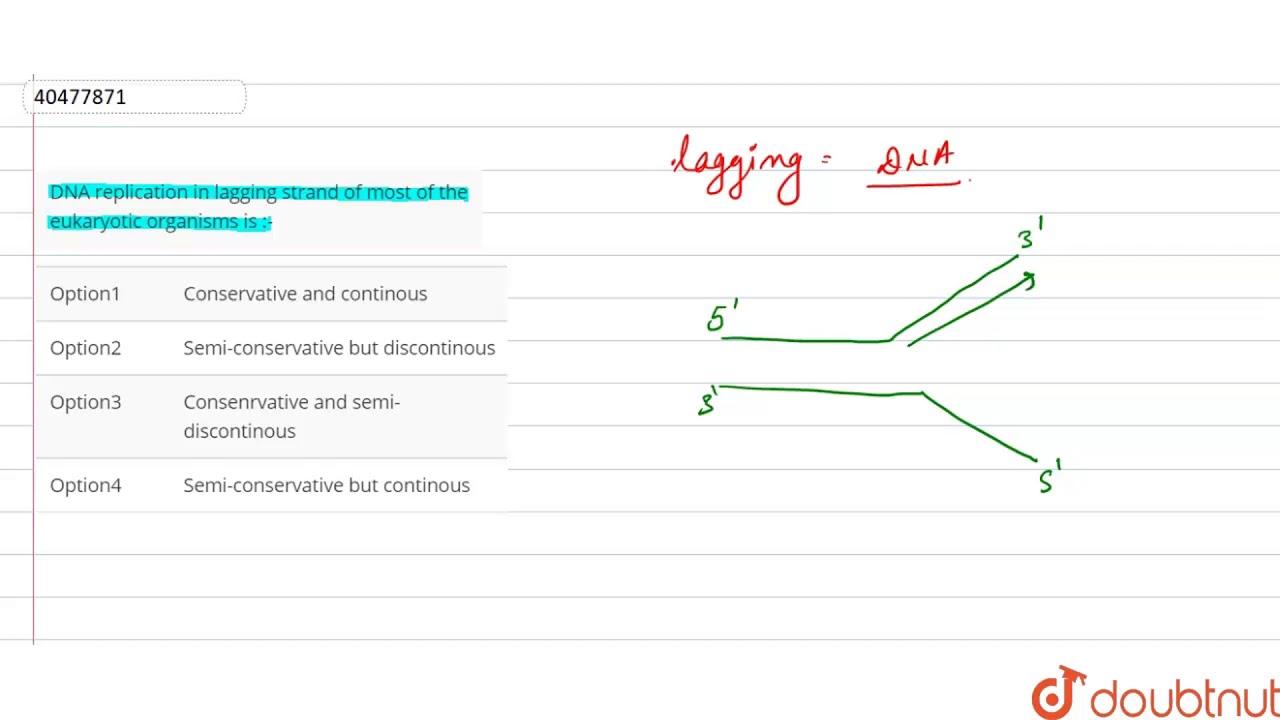
multiple primers needed lagging strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. made in segments lagging strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. daughter strand elongates toward replication fork lagging strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. only one primer needed leading strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. made continuously leading strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. In which image will adenine (A) be the next nucleotide to be added to the primer? leading strand Drag each phrase to the appropriate bin depending on whether it describes the synthesis of the leading strand, the synthesis of the lagging strand, or the synthesis of both strands. Each of the four images below shows a strand of template DNA (dark blue) with an RNA primer (red) to which DNA pol III will add nucleotides. Instead, a primer must pair with the template strand, and DNA pol III then adds nucleotides to the primer, complementary to the template strand. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch. tcggccgt In DNA replication in bacteria, the enzyme DNA polymerase III (abbreviated DNA pol III) adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA. The structure and orientation of the two strands are important to understanding DNA replication. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases. 5' end The DNA double helix is composed of two strands of DNA each strand is a polymer of DNA nucleotides. 3' end The DNA double helix is composed of two strands of DNA each strand is a polymer of DNA nucleotides. Targets of Group 1 can be used more than once.į. The structure and orientation of the two strands are important to understanding DNA replication.ĭrag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram below. Phosphate group The DNA double helix is composed of two strands of DNA each strand is a polymer of DNA nucleotides.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
